Biomedical Waste Management System:
In this article we will discuss about Biomedical Waste Management System.
The learning objectives include: What is biomedical waste and its sources of generation?
It will also help you gain knowledge about the different types of biomedical waste. You can understand the steps of biomedical waste management and also understand the proper mode of collecting and segregating the biomedical waste.
At the end we will also look into the risks associated with biomedical waste, its method of treatment and disposal.
What is Biomedical Waste?
Biomedical waste or our wastes which are generated from diagnosis treatment and immunization center which involves treatment of human beings and animals. They can be solid waste or liquid waste and they post risk.
Why Biomedical Waste Management is important?
The infectivity and the toxicity of biomedical waste pose hazards to human beings and animals that is why its management is very very important.
Types of Biomedical Waste Management:
Based on the source of biomedical waste they are categorized into two types major and minor sources.
Primary health centers, medical college, veterinary college, blood banks, biotechnology institutions, production units, government hospitals, and private hospitals. The wastes generated from these units are categorized under major source likewise under minor sources there are small vaccination centers, psychiatric clinics, funeral services, institutions for disabled persons all leave come under minor sources.
The biomedical waste is broadly classified into non-hazardous and hazardous wastes.
A major portion of biomedical waste is non-hazardous it is about 75 to 90 percent of biomedical wastes are not hazardous, it is not risky and it is similar to domestic waste generally these are generated from the administration and maintenance of hospitals and healthcare premises.
Hazardous waste constitutes about 10 to 20 percent of the overall biomedical waste they are infected as well as toxic. That is why it forces Major Hazard to the environment.
Hazardous wastes are against subcategorized into seven types:
First one infectious waste: Waste which contained pathogens are called infectious waste. For example laboratory cultures waste isolated from warts tissue equipment which are in contact with infected patients and their excreta.
Second, are pathological wastes and human tissues or fluids. Body parts, blood and other body fluids are categorized under pathological waste. For example expired medicine contaminated pharmaceuticals are categorized under pharmaceutical waste.
Waste which is specially generated from cytostatic drugs that are used in cancer are generally termed as title psycho static drugs, they are categorized under toxic chemicals waste, containing chemical substances example disinfectant solvents that are expired and are no longer needed are categorized as chemical wastes.
The next type of wastes are batteries, thermometers, blood-pressure pressurized containers, gas cylinders, gas cartridges, and aerosol cans these are categorized under wastes that contain a high content of heavy metals.
The last type of waste is radioactive waste: Waste containing radioactive substances for example unused liquids generated from laboratory during research, contaminated glassware packages, urine and excreta from patients who are treated with radioactive waste categorized under radioactive waste.
Four major steps of Biomedical Waste Management:
- Segregation collection
- Storage transportation
- Treatment
- Disposal.
Need for Biomedical Waste Management:
Infectivity and toxicity make biomedical waste more hazardous and its management is very very essential.
First it induces various risks to human health and the surrounding ecosystem. It leads to environmental hazards occupational and public hazards that is why it is very very important for proper biomedical waste management.
Biomedical waste management includes four steps:
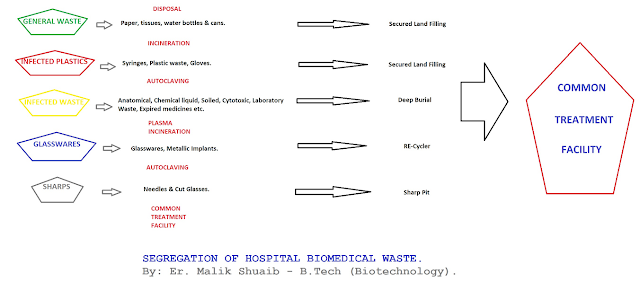
1. Segregation: Segregation is nothing but the simple separation of waste into different categories according to the categories they are segregated and dumped into a different bag which are color-coded. Segregation reduces special needs of waste handling and treatment they avoid mixing biomedical waste along with other municipal wastes, they avoid legal reuse of materials like used syringes needles and other plastics it offers a chance for recycling certain components of medical waste like plastics after proper disinfection. Recycle plastic materials can be used for non-food application purposes.
The biodegradable waste can be composted and also it can be used for composting purpose now based on the segregation the waste or the biomedical waste are segregated into ten different categories:
The table given here summarizes there are ten different categories of biomedical waste based on the segregation party.
- Category 1: Category 1 includes human anatomical waste.
- Category 2: Covers animal waste especially the tissues organs body parts carcasses bleeding parts fluid blood which are generated from veterinary hospitals colleges and animal houses.
- Category 3: Includes microbiology and technology waste: Waste which is generated from laboratory cultures stocks or specimens of life microorganisms or attenuated vaccine, waste from the production of biological toxins are also included under this category.
- Category 4: Includes all waste shafts. Shafts are nothing but leaders syringes capsules scalpel blades etc
- Category 5: Includes discarded medicine and cytotoxic drugs.
- Category 6: Includes soiled ways soil weights are nothing but items contaminated with body fluids including cotton dressings plaster linens bedding and other materials contaminated with blood.
- Category 7: Includes wastes that are generated from disposable items apart from waste shafts all other items are included in this category which includes tubing intravenous catheters etc.
- Category 8: It includes liquid waste wastes that are generated from laboratory washing cleaning housekeeping and disinfecting activities.
- Category 9: Deals with ash generated from incinerators while in generating biomedical waste.
- Category 10: It includes chemical waste all chemicals which are used in the production of biologicals chemicals and other disinfectants example insecticides are categorized under this.
Collection of Biomedical Waste:
Use of different types of containers for different sources of biomedical waste. The container bins should be located in such a manner that a hundred percent collection is achieved the bins and they should carry the biohazard symbol which will represent the nature of the waste figure.
The biomedical waste should be placed in a proper place. They should be segregated into different categories and put in respective designated containers. Now each container should be clearly labeled and they should be kept aside. The reason for labeling is that it may be necessary to trace the waste back to its source. The storage spot always should be on a noticeable area with respective warning signs. The extent of storage should not go beyond 8 to 10 hours in big hospitals which include almost more than not 250 beds and the storage time should be less than 24 hours.
This flow chart provides the color coding for collection of biomedical waste as shown here:
- Yellow color plastic bags include wastes that are generated or which are categorized under 1, 2, 3 & 6.
- Red color bag contains wastes which are categorized under 3, 6 & 7.
- Blue and white translucent plastic bags are used for storing wastes that are categorized under 4 & 7.
- Black color plastic bags are used for category waste which are 5, 9 and 10.
Now after segregation and collection it is important how do you transport the waste.
2. Storage Transportation: Transportation plays an important role. Biomedical waste is transported in two ways either in trolleys or in enclosed. The bags of containers should be tight or littered before hauling into a different place. Special vehicles should be used to avoid contact and direct contact with the transportation operators, scavengers and public. The driver should be trained in such a way that in case of accident he should be able to attend to the spillage.
This figure shows the trolley where the different color-coded bins are being carried off.
There is a second type of vehicle called as wheelbarrows.
Two types of wheelbarrows are there: one is covered and the other one is open.
It is always made up of steel and it is provided with a handle only packed waste in plastic bags. It should be taken to prevent the liquid waste from spilling into the wheelbarrow.
Wheelbarrow can be made of stainless steel with a self-closing lid. It should be sterilized every day with formaldehyde gas. The contaminated linen that is contaminated with blood or other body fluids from each flow must be bundled in a soiled linen or a plastic bag before expelling into the chilled.
Now dust bins are again color-coded and they are used in the storage of biomedical waste dust bin should be placed at a specific site so that they do not overflow between each cycle of waste collection. It should be clean subsequently at each cycle with a proper disinfectant. The dust bins should be wrinkled with plastic bags that are chlorine-free and color-coded as per the law.
3, 4. Treatment and disposable method: Before final disposal the biomedical waste must be disinfected all anatomical waste and can be disposed of by deep barrier syringes to be cut and chemically disinfected with 1% bleaching powder at the source of generation before final disposal into shark pits.
Autoclaving of plastics is done that are infected and are sent into municipal dumps for final disposal.
The incineration method is done to minimize organic (or combustible) waste to inorganic in-combustible matter. Incineration is done at a high temperature of about 900 to 1100 degrees Celsius. It is a dry oxidation process that results in a significant reduction of waste volume and weight the process is usually selected to treat waste which cannot be recycled reused or disposed of.
Now pressurized gas containers, chemical waste, silver salts, photographic or radiographic waste, halogenated plastics such as PVC waste with high mercury or cadmium content, broken thermometers, second-hand batteries, lead-lined wood panels, sealed ampules or ampules containing heavy metals should not be incinerated in an incinerator.
Disadvantages of incineration: there is a considerable release of atmospheric pollutants due to incineration also it needs for the cyclic of slag and dirt that results from incineration. Inadequacy in demolishing anti-thermal chemicals and drugs such as cytotoxic makes it the biggest disadvantage of this method.
Next type of treatment method is autoclave: Autoclaving of biomedical waste is been popularly practiced. It is used to disinfect and treat biomedical waste the biomedical waste was subjected to following temperature and pressure based on its residence time. If the autoclave residence time is not less than 60 minutes the temperature should be less than 121 degrees Celsius with a pressure of 15 pounds per square inches or PSI. If the autoclave residence time is not less than 45 minutes the temperature should not be less than 135 with a pressure of 31 psi.
Likewise if the autoclave residence time is not less than 30 minutes the temperature should not be less than 149 degrees Celsius with a pressure of 52 psi while opening in a vacuum autoclave medical waste is first subjected to a minimum of one free vacuum autoclave. The autoclave with air heating may kill the approved biological indicator at the maximum design capacity of the autoclave unit. The biological indicator of an autoclave unit is bacillus sterile thermophilic spores they are called as spore dials or sports strips with at least 1 into 10 to the power of 4 sports per ml. Hence the temperature must be less than 121 degrees Celsius or a pressure must be less than 15 psi. The chemical indicator strip or tape alters the color which confirms that the respective temperature has been reached it may be essential to use more than one strip over the waste package at various locations to ensure that the inner content of the package has been effectively autoclaved.
(All content and images are for educational purpose).
Thanks...





















0 Comments:
Post a Comment
If you have any doubt kindly let us know.